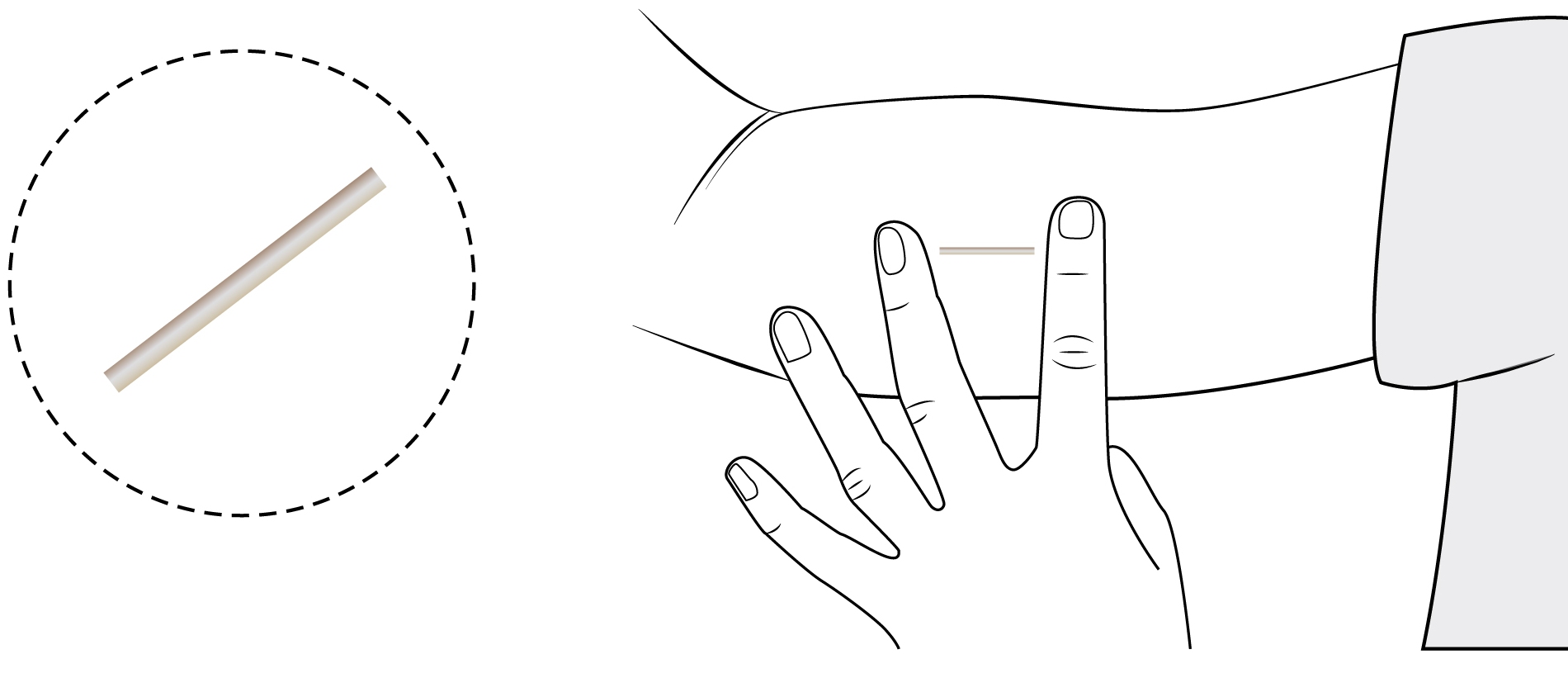
Implant under the skin
The implant is a hormonal contraceptive with a long action span. It consists of a small, very fine stick made of synthetic material containing a progestin hormone, which is regularly diffused in low doses.
How it works
- It inhibits ovulation by keeping the ovaries in a resting period.
- It acts on the womb lining which is no longer prepared for a possible egg implantation.
- It thickens the secretions of the neck of the womb (cervix), thus creating a barrier against sperm.
How it is used
- The implant is put in place under local anaesthetic by the doctor during the first few days of the monthly cycle or during the pause between 2 packets of pills.
- It is placed just under the skin on the inside of the arm.
- The contraceptive effect begins 8 hours after it has been put in place and lasts for 3 years.
- The implant is almost invisible but can be felt under the skin.
- Depending on the woman’s wishes, but within a period of no more than 3 years, the implant is removed under local anaesthetic.
What you must know
- The progestin contained in the implant usually modifies the cycle: irregular bleeding, usually very frequent during the first few months, then periods becoming infrequent and possibly disappearing.
- Fertility usually returns as soon as the implant is taken out.
Good to know
- The best way to protect yourself from HIV or other sexually transmitted infections is to practise safer sex:
1. Always use a condom, male or female, for penetrative sex (vaginal or anal sex).
2. For more personal sexual advice, do the safer sex check on www.lovelife.ch.
2018, SANTÉ SEXUELLE SUISSE, Fondation suisse pour la santé sexuelle et reproductive; ALECSS Association suisse latine des spécialistes en santé sexuelle, Éducation – Formation – Conseil; faseg, Fachverband sexuelle Gesundheit in Beratung und Bildung
Further information on the topic
- Non-hormonal methods of contraception
- The transdermal patch (skin patch)
- The diaphragm (or cap)
- The female condom
- The male condom
- Benzaltex Spermicide
- The coil (copper; or hormonal)
- The quarterly injection
- Less reliable contraceptive methods
- Natural methods of birth control
- Sterilisation
- Male contraception
- The progesterone-only pill (mini-pill)
- The combined pill (oestrogen and progestogen) with a break
- Emergency contraception
- Vaginal ring
- The estrogen and progestogen pill taken without interruption
