Male genital organs
Information: The page "genital organs" will be revised shortly.
The outer parts of the male genital organs (sex) are the penis and two testicles. The inner parts are the vas deferens, the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles.
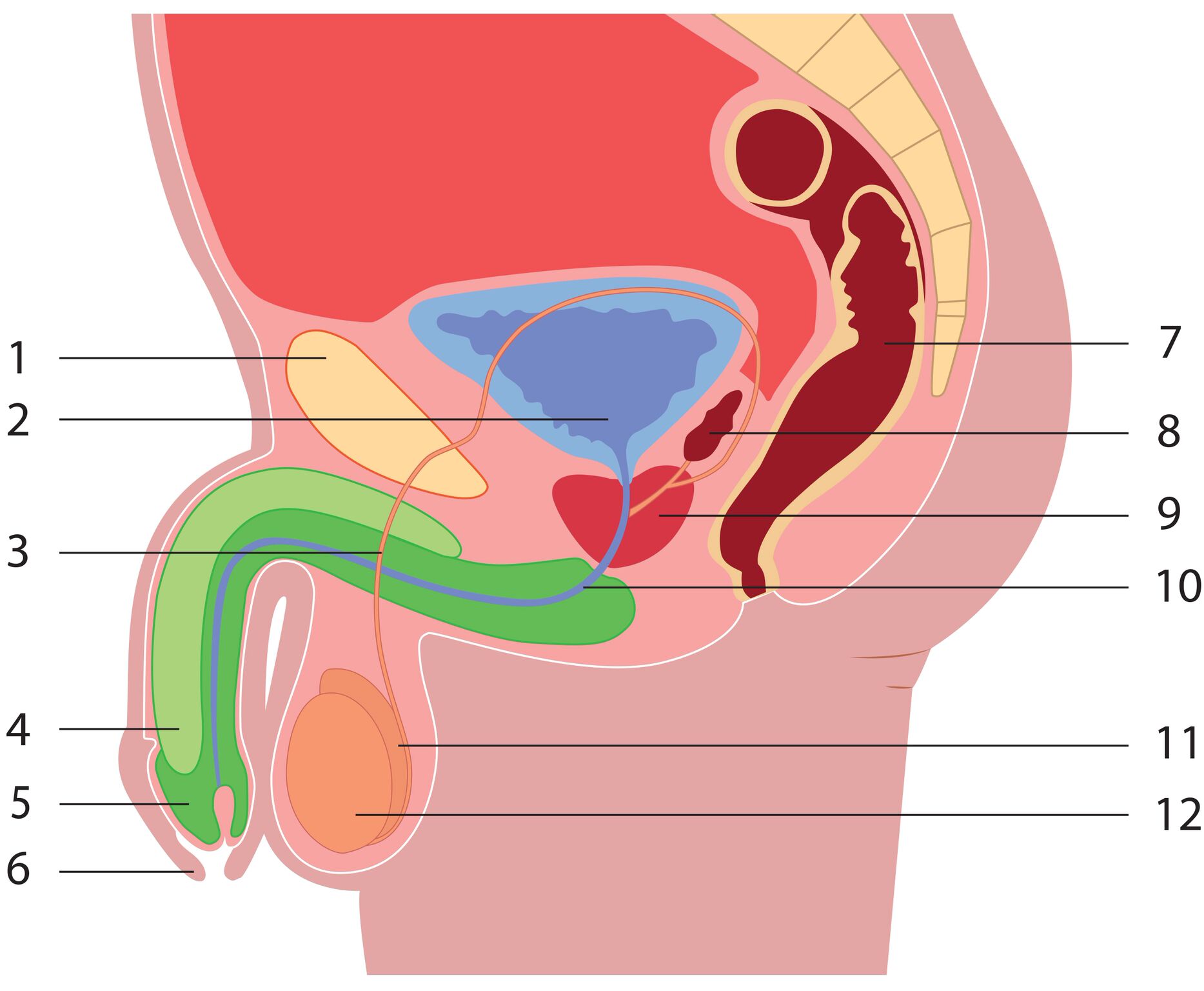
- pubic bone
- bladder
- vas deferens
- erectile tissue of penis (corpus cavernosum penis)
- glans of penis
- foreskin
- rectum (back passage)
- seminal vesicle
- prostate gland
- urethra
- epididymis
- testicle
The testicles
The testicles have two functions:
- constant production of spermatozoa from puberty until death.
- production of male hormone called testosterone.
From each testicle the vas deferens carry the spermatozoa to the penis.
The penis
Allows the passage of urine and sperm. With sexual excitement, it becomes rigid. This erection is caused by a flow of blood and it permits the penetration of the penis into the vagina.
The sperm
The sperm is constituted of spermatozoa and a liquid produced by the prostate and the seminal vesicles. Ejaculation is when sperm spurts out of the penis.
Important !
During erection and before ejaculation the penis discharges a liquid that may contain spermatozoa. Withdrawing before ejaculation will therefore not keep you from getting pregnant. For the same reason, if you use condoms, they must be put on before any contact between the vulva and the penis.
2013, SANTÉ SEXUELLE SUISSE, Fondation suisse pour la santé sexuelle et reproductive; ALECSS Association suisse latine des spécialistes en santé sexuelle, Éducation – Formation – Conseil; faseg, Fachverband sexuelle Gesundheit in Beratung und Bildung
