Female genital organs
Information: The page "genital organs" will be revised shortly.
The outer part of the female genital organs (sex) is the vulva. It is formed of labia (lips) which rim the vagina and the urethra. Urethra is a thin tube that carries urine from the bladder. Passing over the urethra is the clitoris, a small sensitive organ which plays an important role in sexual excitement.
If a woman or a girl has had female genital cutting (excision), the vulva may appear different. Further information at www.female-genital-cutting.ch.
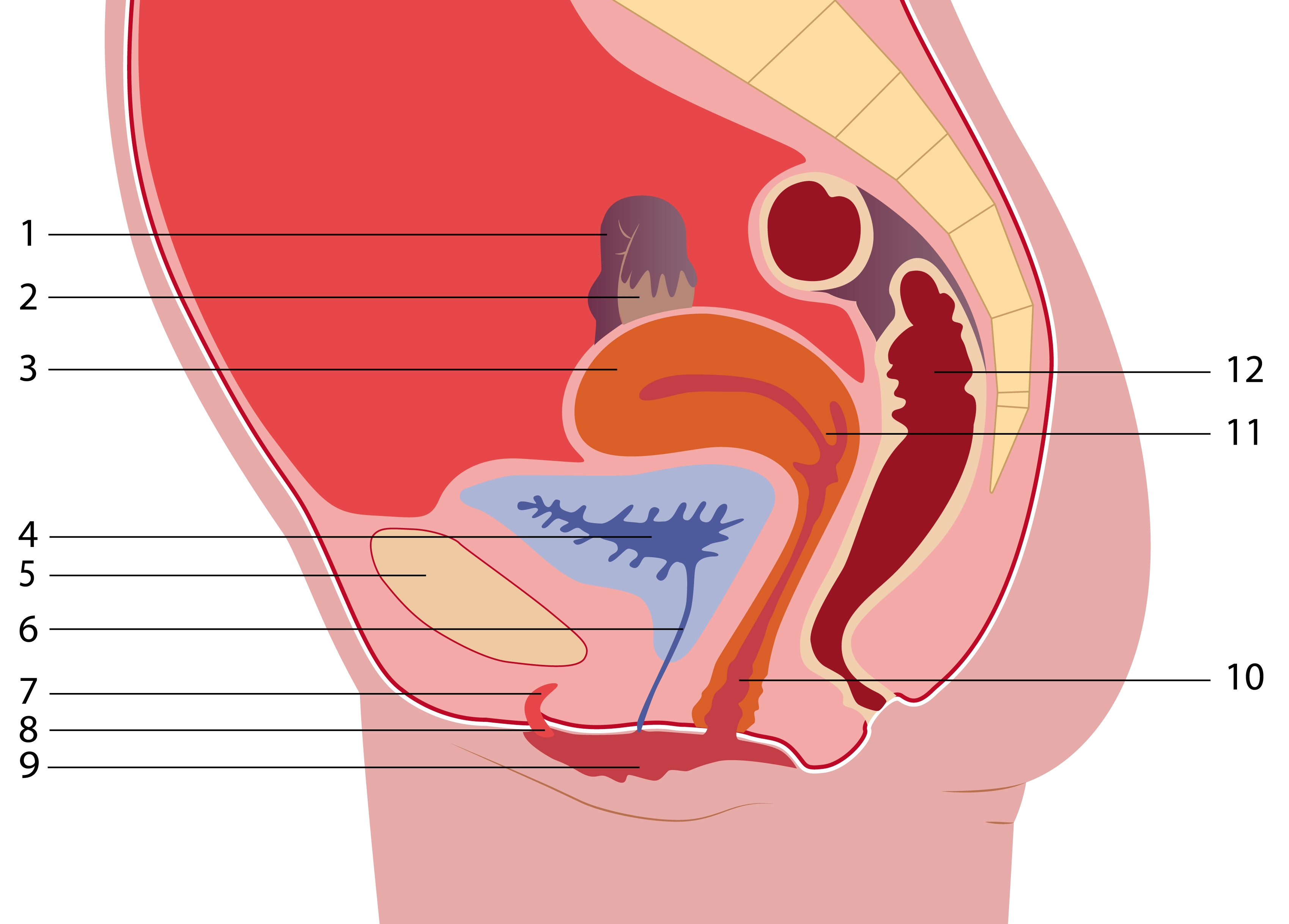
1. fallopian tube
2. ovary
3. uterus (womb)
4. bladder
5. pubic bone
6. urethra
7. erectile tissue of clitoris (corpus cavernosum clitoris)
8. clitoris
9. inner and outer lips of vulva
10. vagina
11. cervix (neck of womb)
12. rectum (back passage)
The vagina
Is a supple tube 7 to 10 cm long. It is where the man’s penis enters during sexual intercourse. It is very elastic so it can stretch around the baby during labour. It also carries the menstrual blood. Sexual desire produces the lubrication of the vagina, which facilitates penetration.
The hymen
Is a thin membrane partly open and situated at the entrance of the vagina, that women have when virgins. Its shape is different from one woman to another. Some women do not have a hymen. Generally it breaks during the first sexual intercourse.
The uterus
It is where the foetus and pregnancy develop. It looks like a pear upside down. In the womb a thin layer of mucus called the endometrium grows each cycle. When you are pregnant, the endometrium forms a nest for the embryo but if fecundation does not take place, it is shed through the monthly period. The lower part that joins the vagina to uterus is called the cervix. It is a small opening that allows the passage of menstrual blood and sperm. At birth time, the cervix and vagina open and stretch to make a passage for the baby.
The ovaries
There are two ovaries, each about the size of an almond and its shape. They have two functions:
- They produce sexual hormones called oestrogen and progesterone, which regulate the cycle.
- They produce a mature egg cell once a month (ovulation).
The fallopian tubes
These are two thin tubes between 10 to 15 cm long that connect the uterus to the ovaries which receive the ovules. The fecundation takes place there. The fertilized egg then goes down to the uterus.
The female cycle
It is time elapsed between the first day of the monthly period and the first day of the next monthly period. The cycle can last from 21 to 35 days. Periods begin around the age of 11 to 15 and ends between the age of 45 to 55. The end of the cycle is called the menopause.
At each cycle, the uterus prepares itself for an eventual pregnancy by the growth of the endometrium. Ovulation takes place 15 days before the next monthly period. Sexual intercourse around the time of ovulation is the best moment to get pregnant.
Ovulation does not always happen at the same moment, the Ogino method (or «safe») is therefore not very reliable if you want to avoid a pregnancy.
During periods...
...you can take baths, showers and wash your hair. You can also exercise and go swimming (using tampons).
2017, SANTÉ SEXUELLE SUISSE, Fondation suisse pour la santé sexuelle et reproductive; ALECCS Association suisse latine des spécialistes en santé sexuelle, Éducation – Formation – Conseil, faseg, Fachverband sexuelle Gesundheit in Beratung und Bildung
